Loan Amortization refers to the systematic repayment of a debt over an extended period through a series of scheduled installments. To amortize a loan effectively, the periodic payments must be substantial enough to cover not only the interest that has accrued but also a portion of the principal amount.
As per Wiki – “In banking and finance, an amortizing loan is a loan where the principal of the loan is paid down over the life of the loan (that is, amortized) according to an amortization schedule, typically through equal payments.”
In simpler terms, amortization occurs when a borrower repays a debt through regular, equal installments over time. With each payment, a portion is allocated towards the principal amount, while the remaining portion goes towards covering the interest charges. This systematic approach ensures a structured and predictable repayment process, allowing the borrower to gradually eliminate the debt.
It is important to note that interest costs are typically highest at the beginning of the loan tenure, particularly for long-term loans. During the initial stages, a substantial portion of each periodic payment is designated as an interest expense, leaving only a small portion to be applied towards the principal amount. However, as time progresses, an increasingly larger portion of each payment goes towards reducing the principal, while the interest component diminishes.
As time goes on, more and more of each payment goes towards your principal (and you pay less in interest each month).
The process of amortizing a loan typically involves establishing a series of equal monthly payments. This approach provides the lender with two key components:
- Interest calculated based on each month’s unpaid principal balance, and
- Principal repayments designed to ensure that the unpaid principal balance reaches zero by the end of the loan term.
Consequently, while the amount of each monthly payment remains identical throughout the loan tenure, the interest component steadily decreases, and the principal component correspondingly increases.
An amortization schedule is a tabular representation that outlines the repayment breakdown for each payment period of an amortized loan.
Each row in the schedule displays the amount of the payment allocated towards interest, the amount applied towards reducing the principal, and the remaining loan balance at the end of the period.
In essence, an amortization schedule provides a comprehensive overview of the repayment structure, detailing the interest and principal components, as well as the evolving loan balance over time.
Financial institutions and lenders typically incorporate additional information into their amortization schedules, such as tax and insurance payments made on behalf of the borrower, if applicable. This comprehensive approach ensures transparency and enables borrowers to track their loan repayment progress effectively.
To help the understanding and calculation of loan amortization, I have created a user-friendly Loan Amortization Template in Excel format. This template incorporates preset formulas, requiring users to input their specific loan amounts and dates. Subsequently, the template automatically calculates all relevant figures, streamlining the amortization process.
Click here to Download the Loan Amortization Excel Template.
Click here to Download All Personal Finance Excel Templates for ₹299.Additionally, you can download other accounting templates like Cash Book with VAT, Accounts Payable with Aging and Salary Sheet from here.
Let’s discuss the template contents in detail.
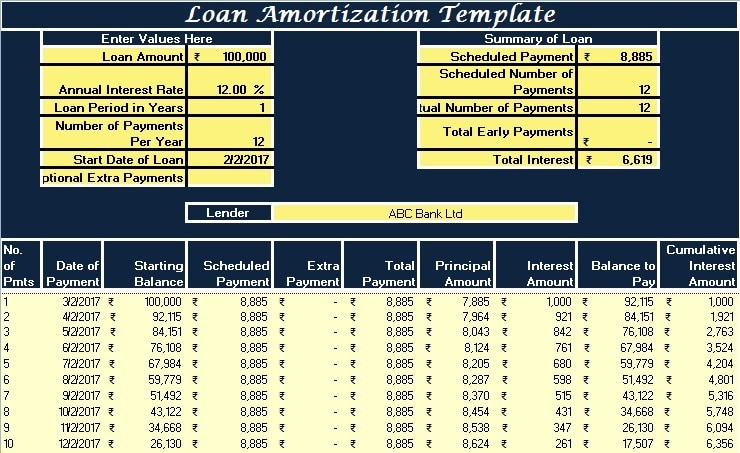
Content of Loan Amortization Template
The first row of the sheet consists of the heading of the sheet.
This template consists of 2 major sections:
- Data Input Section
- Payment Schedule Section
1. Data Input Section
The Data Input Section consists of two columns with predefined formulas. The user is required to enter the necessary data in the column on the left side.
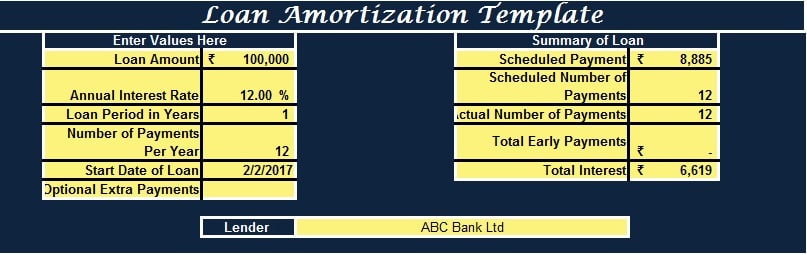
In this section, the user must input the Principal amount they wish to borrow or are planning to borrow. Subsequently, the interest rate charged by the lending bank or institution must be entered.
As payment schedules are typically monthly, the number of payments per year is designated as 12.
The user needs to provide the loan’s start date, which will be used to calculate the repayment dates.
If the user plans to make any additional optional payments alongside their regular installments, they can enter those in the designated Optional Payments cell.
Lastly, the user must enter the name of the Lender or Bank.
The columns on the right-hand side will display the scheduled payment amount, the number of installments, the total interest, and other relevant information.
After entering all the required data, the template will generate the repayment schedule.
It is a straightforward process.
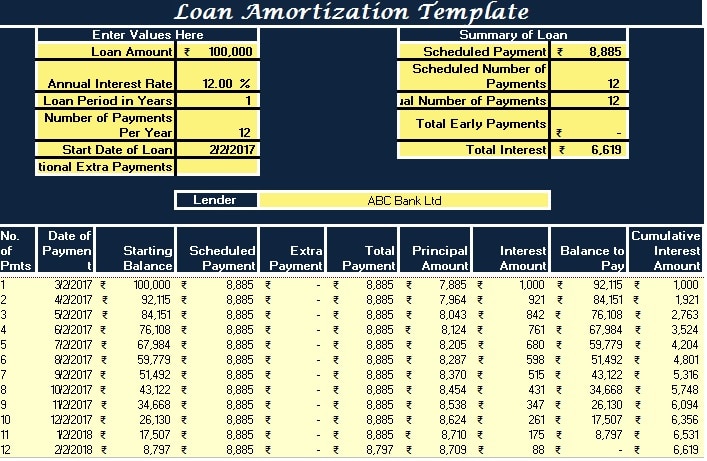
2. The Payment Schedule Section
This section displays the payment schedule, which is generated once the user enters the details in the Data Input Section.
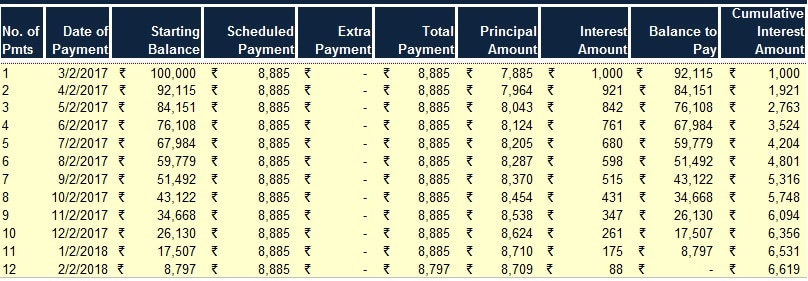
The payment schedule will automatically show the scheduled repayment dates, the beginning balance, total payment, interest and principal payments, and the ending balance for each period.
We express our gratitude to our readers for their continued support and engagement through likes, shares, and follows on various social media platforms, particularly Facebook.
If you have any queries or questions, please share them in the comments section below. I will be pleased to assist you.