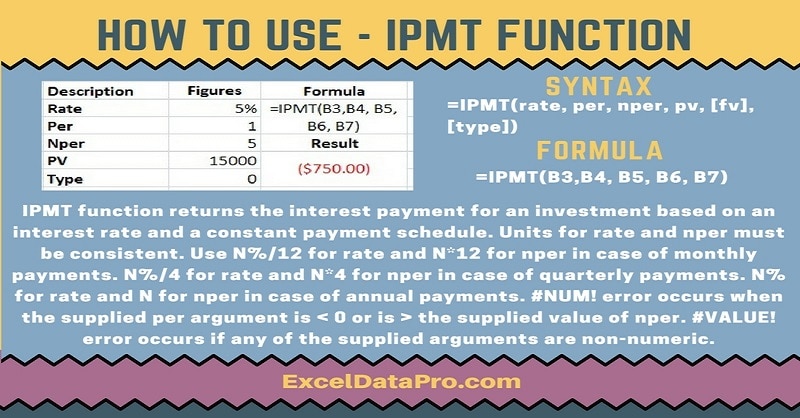
IPMT function returns the interest payment for an investment based on an interest rate and a constant payment schedule.
In other words, It calculates the interest payment, during a specific period of a loan or investment that is paid in constant periodic payments, with a constant interest rate.
The IPMT function is an inbuilt function in Excel. It falls in the category of Financial Functions. It is a worksheet function as well as a VBA Function.
As a worksheet function, you can enter it as part of a formula in a cell of a worksheet.
As a VBA function, you can enter the IPMT function as macro code through the Microsoft Visual Basic Editor.
Syntax for IPMT Function
=IPMT(rate, per, nper, pv, [fv], [type])
Arguments
Rate: The interest rate per period.
Per: The period for which you want to find the interest and must be in the range 1 to nper.
Nper: The total number of payment periods in an annuity.
Pv: The present value, or the lump-sum amount that a series of future payments is worth right now.
Fv: It is an optional argument. The FV or a cash balance you want to attain after the last payment is made.
If FV is omitted, excel assumes it to be 0 (the future value of a loan, for example, is 0).
Type: This is also an optional argument. The number 0 or 1 and indicates when payments are due. If this argument is omitted, excel assumes it to be 0.
The Type argument can be 0 or 1, where:
0 = The payment is made at the end of the period;
1 = The payment is made at the start of the period.
We have created the infographics for the IPMT Function. With the help of these infographics, you can easily learn step by step process for using this excel functions.
Furthermore, Excel consists of many inbuilt functions which are helpful in the analytical and statistical study of number.
Simply follow the instructions in the infographics below:

Please note that, as per the general cash flow convention, all the outgoing payments will be represented by negative numbers. Whereas all the incoming payments are represented by positive numbers.
Units for rate and nper must be consistent.
Use N%/12 for rate and N*12 for nper when there are monthly payments. N%/4 for rate and N*4 for nper when quarterly payments and N% for rate and N for nper when there are annual payments.
Errors
#NUM! error occurs when the supplied per argument is < 0 or is > the supplied value of nper.
#VALUE! error occurs if any of the supplied arguments are non-numeric.
To learn other function like CUMPRINC, ACCRINTM and PRODUCT Functions, please click on the name of the function.
Additionally, you can download other accounting templates like Weekly Timesheet, Salary Sheet and Checkbook Register from here.
We thank our readers for liking, sharing and following us on different social media platforms.
If you have any queries please share in the comment section below. I will be more than happy to assist you.
Leave a Reply