DDB Function calculates depreciation of an asset for a specified period using the double-declining balance method or other methods if specified in the argument.
The double-declining balance method calculates depreciation on accelerated rate. The depreciation amount is high in the first period and goes on decreasing in successive periods.
The declining balance method is named as it reduces an asset’s value by the amount it depreciated in the previous years.
You will calculate the new depreciation based on that lower value. Hence it is given the name as declining balance method.
This rate will reduce the cost of the asset down to its salvage value after the specified period.
The DDB function is an inbuilt function in Excel. It falls under the category of Financial Functions.
DDB is both a worksheet function as well as a VBA function.
As a worksheet function, you can use the DDB function as part of a formula in a cell.
As a VBA function, this function can be used in macro code which you can enter through the Microsoft Visual Basic Editor.
To calculate the Straight Line Depriciation you can use the SLN Function and to calculate the decling method depreciation you can use DB Function.
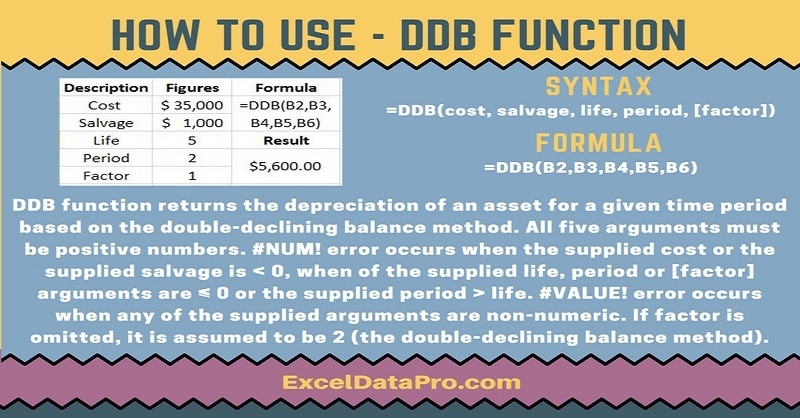
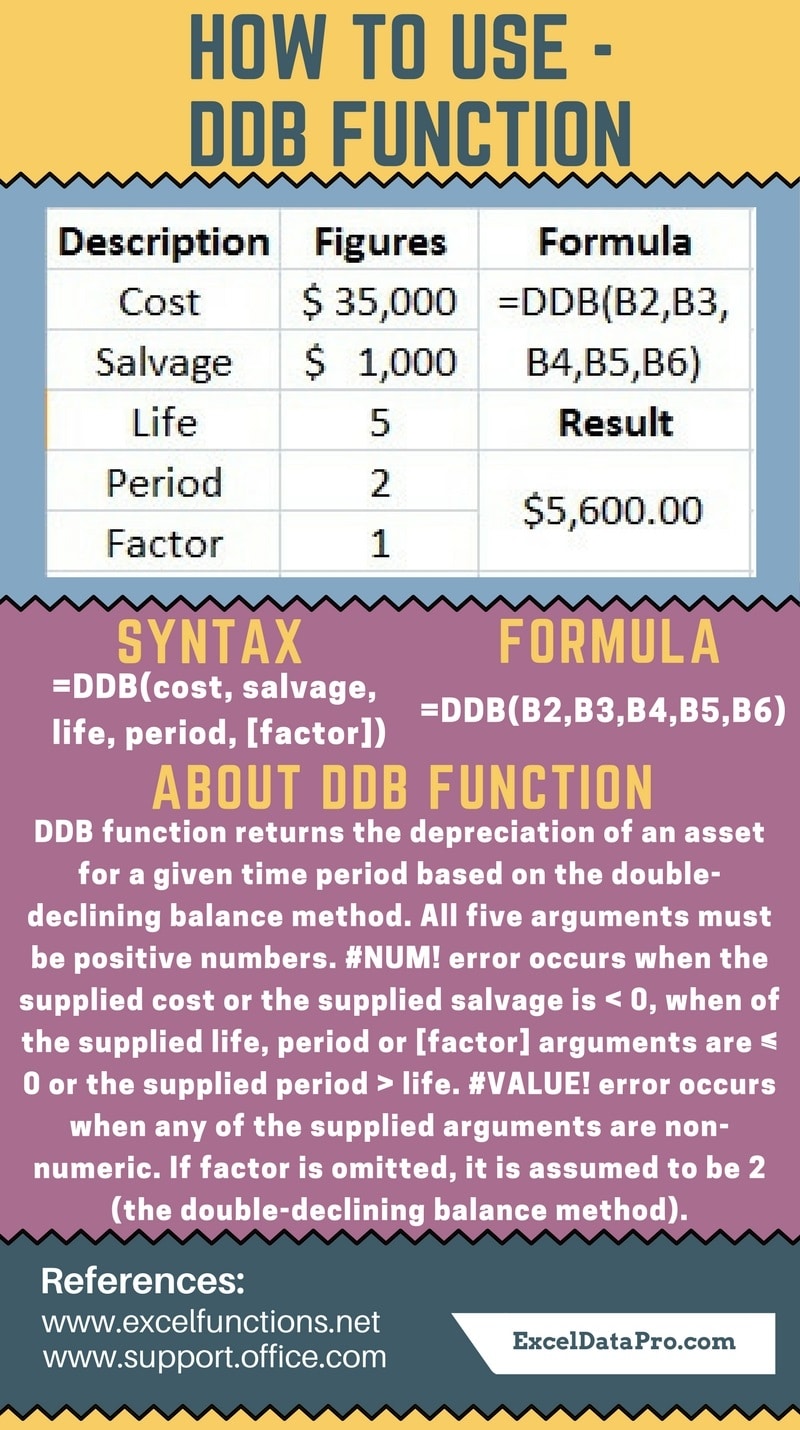
Syntax for DDB Function
=DDB(cost, salvage, life, period, [factor])
Arguments
Cost: Purchase Price or the cost of the asset.
Salvage: Scrap value or the salvage value of the asset after it has been fully depreciated.
Life: Life f the Asset or Usable time period of the asset.
Period: Duration of depreciation. Please make you use same units for life. If the period is in years life should also be in years.
Factor: This is an optional argument. The rate at which the balance declines. If this argument is omitted, it will assume the factor to be 2 (Double Declining Balance Method)
We have created the infographics for the DDB Function. With the help of these infographics, you can easily learn step by step how to use this excel functions.
Furthermore, Excel consists of many inbuilt functions which are helpful in the analytical and statistical study of number.
Simply follow the instructions in the infographics below:
Errors
#NUM! error occurs:
1. When the supplied cost or the supplied salvage is < 0. 2. When the supplied life, period or the [factor] arguments are ≤ 0. 3. When supplied period > life.
#VALUE! error occurs when any of the supplied arguments are non-numeric.
To learn other function like SLN, DB and PRODUCT Functions, please click on the name of the function.
Additionally, you can download other accounting templates like Petty Cash Book, Simple Cash Book and Accounts Payable Excel Templates from here.
We thank our readers for liking, sharing and following us on different social media platforms.
If you have any queries please share in the comment section below. I will be more than happy to assist you.
Leave a Reply