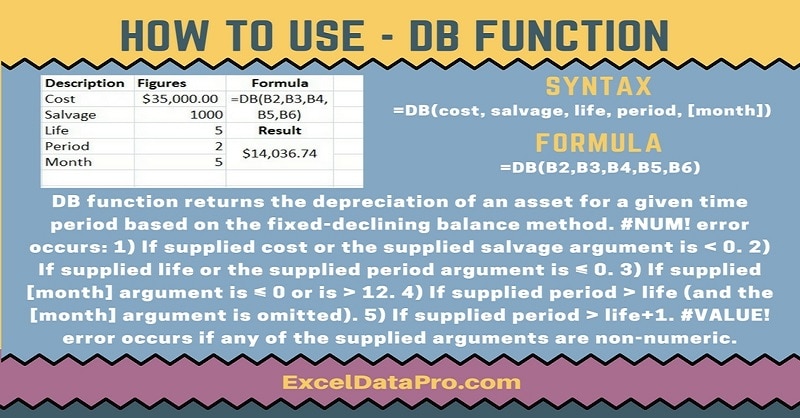
DB Function returns the depreciation of an asset for a specified period using the fixed-declining balance method.
In other words, DB function returns the depreciation of an asset for a given time period based on the fixed-declining balance method.
The declining balance method is named as it reduces an asset’s value by the amount it depreciated in the previous years.
You will calculate the new depreciation based on that lower value. Hence it is given the name as declining balance method.
This rate will reduce the cost of the asset down to its salvage value after the specified period.
The DB function is an inbuilt function in Excel under the category of Financial Functions. You can use the DB function as part of a formula in a cell of a worksheet.
Syntax for DB Function
DB(cost, salvage, life, period, [month])
Arguments
Cost: The initial cost of the asset.
Salvage: The value at the end of the depreciation (sometimes called the salvage value of the asset).
Life: The number of periods over which the asset is being depreciated (sometimes called the useful life of the asset).
Period: The period for which you want to calculate the depreciation. The period must use the same units as life.
Month: The number of months in the first year. If the month is omitted, it is assumed to be 12.
I have created the infographics for the DB Function. With the help of these infographics, you can easily learn step by step process for using this excel functions.
Furthermore, Excel consists of many inbuilt functions which are helpful in the analytical and statistical study of number.
Simply follow the instructions in the infographics below:
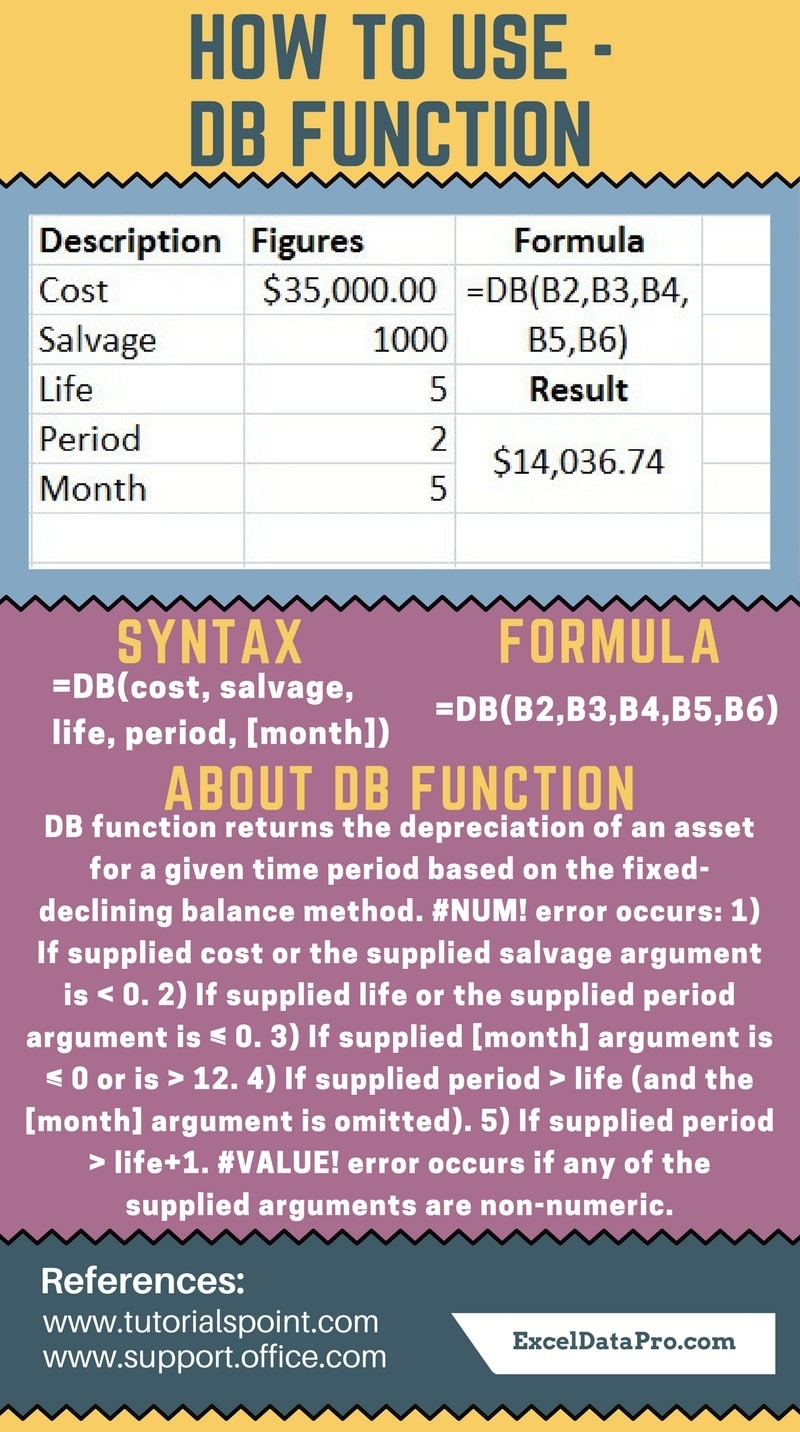
The fixed-declining balance method computes depreciation at a fixed rate. DB uses the following formulas to calculate depreciation for a period:
(cost – total depreciation from prior periods) * rate
where:
rate = 1 – ((salvage / cost) ^ (1 / life)), rounded to three decimal places
For the first period, DB uses this formula:
cost * rate * month / 12
For the last period, DB uses this formula:
((cost – total depreciation from prior periods) * rate * (12 – month)) / 12
Errors
#NUM! error occurs if:
1. Supplied cost or the supplied salvage argument is < 0; 2. Supplied life or the supplied period argument is ≤ 0; 3. Supplied [month] argument is ≤ 0 or is > 12;
4. Supplied period > life (and the [month] argument is omitted);
5. Supplied period > life+1.
#VALUE! error occurs if any of the supplied arguments are non-numeric.
To learn other function like ACCRINT, AMORLINC and ZTEST Functions, please click on the name of the function.
Additionally, you can download other accounting templates like Break Even Analysis Template, Salary Sheet Template and Invoice with GST Template from here.
We thank our readers for liking, sharing and following us on different social media platforms.
If you have any queries please share in the comment section below. I will be more than happy to assist you.